- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of wild pansy in the UK
Distribution and biology of wild pansy in the UK
Wild pansy commonly seen than field pansy but can contaminate grain. Find out how to identify and control this broad-leaved weed.
Overview
Wild pansy (Viola tricolor) is less commonly seen in fields than field pansy. It is found on stony arable land in both winter and spring crops; seeds may contaminate grain and be difficult to clean. Wild pansy is not as competitive as field pansy, but has a similar life cycle; autumn-germinating plants can overwinter and flower early in the following season. The seeds are dispersed from an exploding seed head.
- It has value to biodiversity
Description
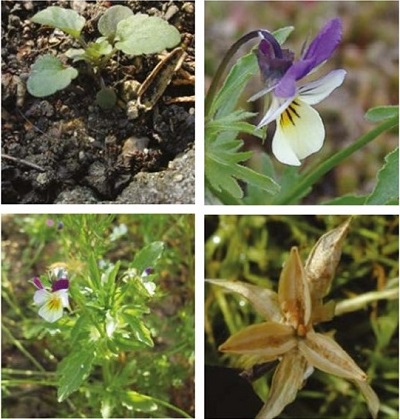
It is an annual or perennial dicotyledon, larger and more robust than field pansy. Leaves are oblong, lobed or toothed with projections at the base. The flowers are five-petalled and blue violet with the lower petals flushed with bright yellow.
Key features
Plant: Wild pansy is larger and more robust than field pansy.
Flowers: The petals are larger than the sepals.

Location and life cycle
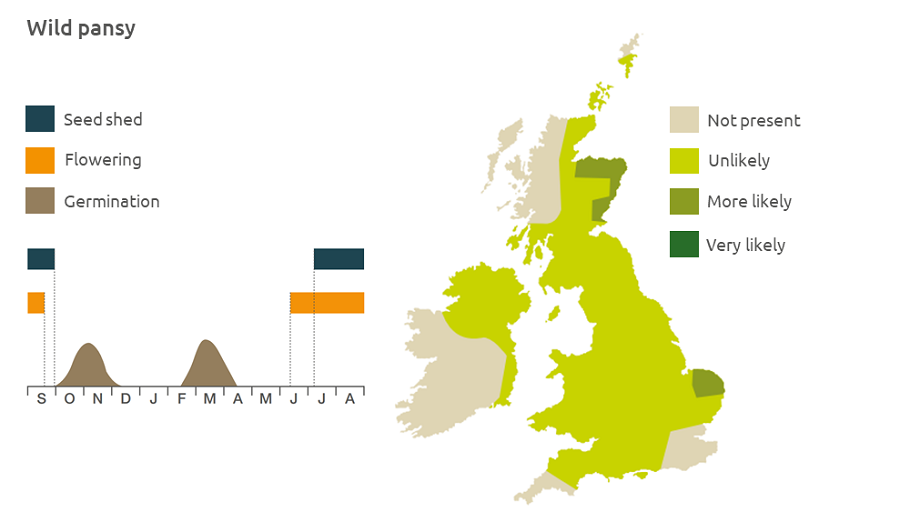
Geographic distribution
Wild pansy can grow to an altitude of 575 m and is found in slightly acidic habitats and cultivated ground, gardens and wasteland. It is most often found in damp cool climates.
Soil type
It grows on sandy, stony and infertile soils, pH range 5–7.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Seed weight: 0.4 mg
Management
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

