- Home
- Knowledge library
- Understanding pneumonia and lung scanning
Understanding pneumonia and lung scanning
Pneumonia is one of the most common causes of calf mortality and poor performance in youngstock. It often develops subclinically (without obvious symptoms), making it difficult to detect and frequently underestimated on farms.
Treatment costs range between £30 and £80 per case, and calves with lung scores greater than 3 can cost a dairy enterprise £500–£1,500 over their lifetime.
Causes of pneumonia
- Presence of bacteria and viruses
- Environment – cold and wet weather, poor ventilation
- Stress – weaning, group changes or disbudding
- Low immunity at birth
Impacts on herd performance
- Reduced feed conversion efficiency
- Reduced daily weight gain
- Lower tolerance to high temperatures
- Increased risk of secondary infection
Learn more about pneumonia in calves
Why lung scan?
Calves with damaged lungs may not cough or show other expected signs of disease.
Lung scanning allows early detection and proactive treatment of subclinical disease before it develops.
When to scan
First lung scans are usually done at weaning to assess pneumonia prevalence. Calves over three months old or weighing more than 150 kg cannot be scanned effectively, as ultrasound penetration is limited to 12 cm.
Pneumonia risk increases at stressful times. If many cases occur at weaning, consider scanning calves earlier, for example at disbudding, to identify when infection risk is highest and make management changes accordingly.
The frequency of visits will depend on:
- Prevalence
- Calf numbers
- Calving pattern
Once a scanning plan has been established and more visits are completed, you can calculate how treatments or management changes affect pneumonia levels in the herd.
Benefits of lung scanning
- Non-invasive and fast
- Measures and monitors respiratory disease prevalence on farm
- Enables earlier identification of disease for better treatment outcomes
- Identifies at-risk groups and potential causes
- Supports selection of herd replacements
- Targets treatment, supporting responsible antimicrobial usage
- Assesses on-farm disease detection rates
See how lung scanning led to a healthier herd at Rough Grounds Farm
Understanding scan results
Calves will be scored from 0 (healthy) to 5 (multiple affected lung areas) using the Wisconsin calf scan score chart.
The severity and duration of disease affects the extent of lung damage and the amount of consolidation seen.
Score Result
0 Healthy lung, no signs of disease
1 Limited comet tailing
2 Comet tailing, small areas of consolidation
3 One lobe consolidated
4 Two lobes consolidated
5 Three or more lobes consolidated
Source: Adapted from the Wisconsin score chart
Comet tailing describes the shapes seen on the ultrasound image caused by fluid or gas bubbles. These occur when the ultrasound pulse bounces off fluid or gas bubbles and returns to the probe.
Ultrasound appearance
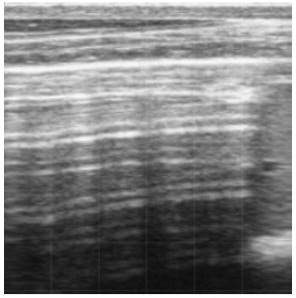 Shropshire Farm Vets
Shropshire Farm Vets
Score 0 – Healthy, aerated lungs
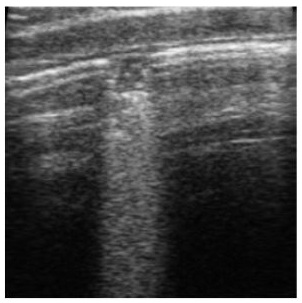
Score 2 – Small areas of consolidation
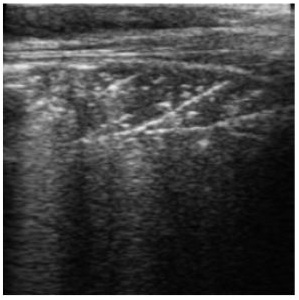
Score 3 – Larger areas of consolidation
In calves showing signs of lung damage, act quickly to prevent further damage and discuss appropriate treatment with your vet.
Key findings from 500 calves scanned three times:
- 5–10% of calves had lung lesions on 'good' farms
- 20–30% of calves had lung lesions on 'poorer' farms
- 75% of calves scoring 2 or 3 recovered within a fortnight
- Score 2 calves had a high recovery rate
- Score 3 calves had permanent scarring, but early detection improved outcomes
- Successful treatment of a calf scoring 3 or higher could save £1,500
James Marsden, Director at Shropshire Farm Vets, is seeing good uptake of lung scanning, with 500–1,000 calves expected to be enrolled into the programme each year.
This data supports further studies into the effects of lung lesions on productivity, including age at first calving, as part of a Diploma in Bovine Reproduction (DBR).
Thanks to Shropshire Farm Vets for supplying their lung-scanning data and images.
Managing pneumonia
Prevention is better than cure. Work with your vet to identify areas within your housing or rearing protocols that may increase the risk of pneumonia.
Key prevention tips:
- Bedding: Keep plentiful, clean and dry
- Colostrum: Provide good-quality colostrum quickly for strong immunity
- Hygiene: Clean and disinfect shared equipment to minimise transmission. Review herd health plans with your vet
- Stress management: Minimise the simultaneous occurrence of stressful events, such as weaning, group changes and disbudding
- Vaccination: There are several vaccines available in the UK targeting individual or specific pathogens. Discuss with your vet for appropriate action
- Ventilation: Ensure a good flow of fresh air without causing draughts to remove pathogens and excess moisture in calf housing

